The word greenhouse effect has been discussed on a very wide range in this new era. Even this being a heated discussion, very few of us know what it is and the causes of greenhouse and its effects. Let’s bring in here all these subjects under a single topic for a better understanding of what is greenhouse effect, its causes and effects.
What is Greenhouse effect?
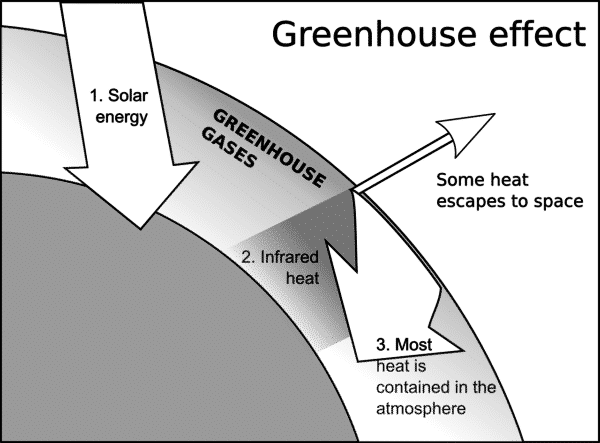
The Greenhouse effect is a process through which the Earth surface remains warm. The solar energy reaches the Earth’s atmosphere from the Sun. Some portion of this energy is radiated back into space and the rest is absorbed by the greenhouse gases.
Water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone and artificial chemicals such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are the primary greenhouse gases present in Earth’s atmosphere.
The absorbed energy warms the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth. This effect keeps the temperature of Earth around 33 degrees Celsius and allowing life on Earth to exist.
Now due to the human activities (the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation), the natural greenhouse effect has increased, resulting global warming.
History
The existence of the greenhouse effect was remarked by Joseph Fourier. In 1859, Irish physicist John Tyndall proved that some gases have a remarkable capacity to hang onto heat, thus demonstrating the basis of the greenhouse effect. Svante Arrhenius, Swedish scientist was the first to claim that fossil fuel combustion may result in enhanced global warming. The term “Greenhouse” was first used by Nilis Gustaf Ekholm in 1901.
Mechanism
The Earth receives energy from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation but mostly is in the form of visible light and infrared. About 30 percent of the energy is reflected back and remaining energy is absorbed by the Earth’s surface. This energy keeps the Earth warm.
The heat is then radiated from the Earth into space but the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere traps this heat. This process helps to sustain life here.
But the activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation are increasing the amount of greenhouse gases released into the atmosphere. Due to this reason, extra heat is trapped in the atmosphere and thus the Earth’s temperature rise.
Causes of the Greenhouse Effect
- Burning of fossil fuels:
Fossils fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas have become an important part in human’s life. The fuels are used on large basis to generate electricity and for transportation. When they are burnt, the carbon stored in them is released which reacts with oxygen in the air to form carbon dioxide. The number of vehicle is increased with the increase in the population and has resulted in the increase in the pollution in the atmosphere. These vehicles while running, release carbon dioxide which is one of the main gas responsible for the greenhouse effect.
The emissions are high while producing electricity because still coal is used for the generation which releases large amount of carbon dioxide. Still it is the primary sources for the production. Though renewable sources are available, it may take a time before reducing the dependence on coal.
- Deforestation:
The major portion on the Earth’s surface is covered by forest. Plants and trees take carbon dioxide and releases oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. The large scale development has resulted in clearing the forest by cutting down the trees so people could occupy the land for living. The stored carbon in wood is converted into carbon dioxide while burning.
- Increase in population:
There has been tremendous growth in population over the last few decades. This has increased the demand for food, cloth and shelter. The increased demand brought Industrial Revolution which caused the release of harmful gases like CFCs into the atmosphere. Also, more people means more usage of the fossil fuel which in turn increases the greenhouse effect.
- Farming:
The fertilizers are intensively used in agriculture which has nitrous oxide, one among the greenhouse gases which causes the greenhouse effect. This leads to global warming.
- Industrial waste and landfills:
Since the Industrial Revolution, the industries have tremendously increased and new technologies are implemented for the manufacturing of the various products. Industries which are involved in cement production, fertilizers, coal mining, oil extraction produce harmful greenhouse gases.
Landfills filled with garbage produce carbon dioxide and methane gases contributing to the greenhouse effect.
Effects (Outcome)
The increased greenhouse gases due to the human activities have many consequences in the climate change.
- Global warming:
Greenhouse gas levels have been increasing since the Industrial Revolution has started, but over the last few decades the growth has been tremendously rapid. And so the greenhouse effect is enhanced to the point where too much heat is kept in the Earth’s atmosphere. The extra heat trapped has increased the surface temperature by 0.75 degree Celsius over the last 100 years.
Global warming is damaging the environment in many ways:
- Increased melting of ice and snow.
- Sea level rise.
- Stronger storms and extreme natural calamities.
- Ocean Acidification:
The increased level of carbon dioxide has made the oceans more acidic than ever. The ocean serves a sink and absorbs about a quarter of human carbon dioxide emissions, which then goes on to react with seawater to form carbonic acid. Thus as the level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere rises, the acidification of the oceans increases. [Read more about acidification of Ocean]
- Smog and ozone pollution:
Over the last century, global background ozone concentrations have become twice mainly due to the emissions of the methane and nitrogen oxide caused by human activities. At ground level, ozone is an air pollutant, a major component of smog which is dangerous for both human and plants.
Life expectancy has been reduced by the long term exposure to the ozone. Recent studies states that the yield of the key staple crops, like corn, wheat are being reduced due to present day ozone exposure.
- Ozone layer depletion:
Ozone depletion is observed since the late 1970s: a steady decline of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth’s stratosphere. CFCs are referred to as ozone-depleting substances (ODS). The ozone layer prevents most harmful ultraviolet light from passing the Earth’s atmosphere. The projected decreases in ozone generated worldwide concern, leading to adoption of the Montreal Protocol which bans the production of CFCs, halons and other ozone-depleting chemicals. A variety of biological consequences such as increase in sunburn, skin cancer, cataracts, damage to plants and reduction of plankton populations in the ocean is resulted from the increased UV light exposure due to ozone depletion.
If the enhanced production of the greenhouse gases is not reduced within the next few decades, it is possible that life on Earth might be difficult for the generations to come. Increase in heat and radiation may make going outside difficult or dangerous during the daytime. These increased energies could affect the entire ecosystem. The plants and animals will become extinct from the global warming. So the renewable energy resources should be used which will reduce the greenhouse effect. And new methods should be explored to save the Earth.
